

Let's generate the HTML output in a separate directory called docs. Verify that you are now checked out to your new branch: git status Notice that although you created a new branch, you are still checked out to master, as indicated by the in-line response from Git.Ĭheck out to your new branch: git checkout Replace with a descriptive name, for example speed-and-distance-report: git branch Ĭheck your repository’s status: git status
Click Help, About RStudio to check the current version.Ĭreate a new branch. Note: if you cannot find the Terminal tab, check if you use RStudio version 1.1.383 or higher. The Terminal tab is next to the Console tab. In RStudio click the Terminal tab in the lower left pane.As RStudio currently does not support local branches very well, we will use Git from the command-line in RStudio. Let’s make a couple of more changes in your project using the steps of GitHub Flow.
#R studio tutorial code#
On GitHub, navigate to the Code tab of the repository to see the changes. Click the Push button to push your changes to the remote repository. 
Click the Pull button to fetch any remote changes.Add a commit message, for example Add initial speed and distance report.In the Review changes view, check the staged box for all files.In RStudio click the Git tab in the upper right pane.Enter speed-and-distance and click Save.Īfter you have created the R Markdown document and finished making your changes, it is time to commit them.
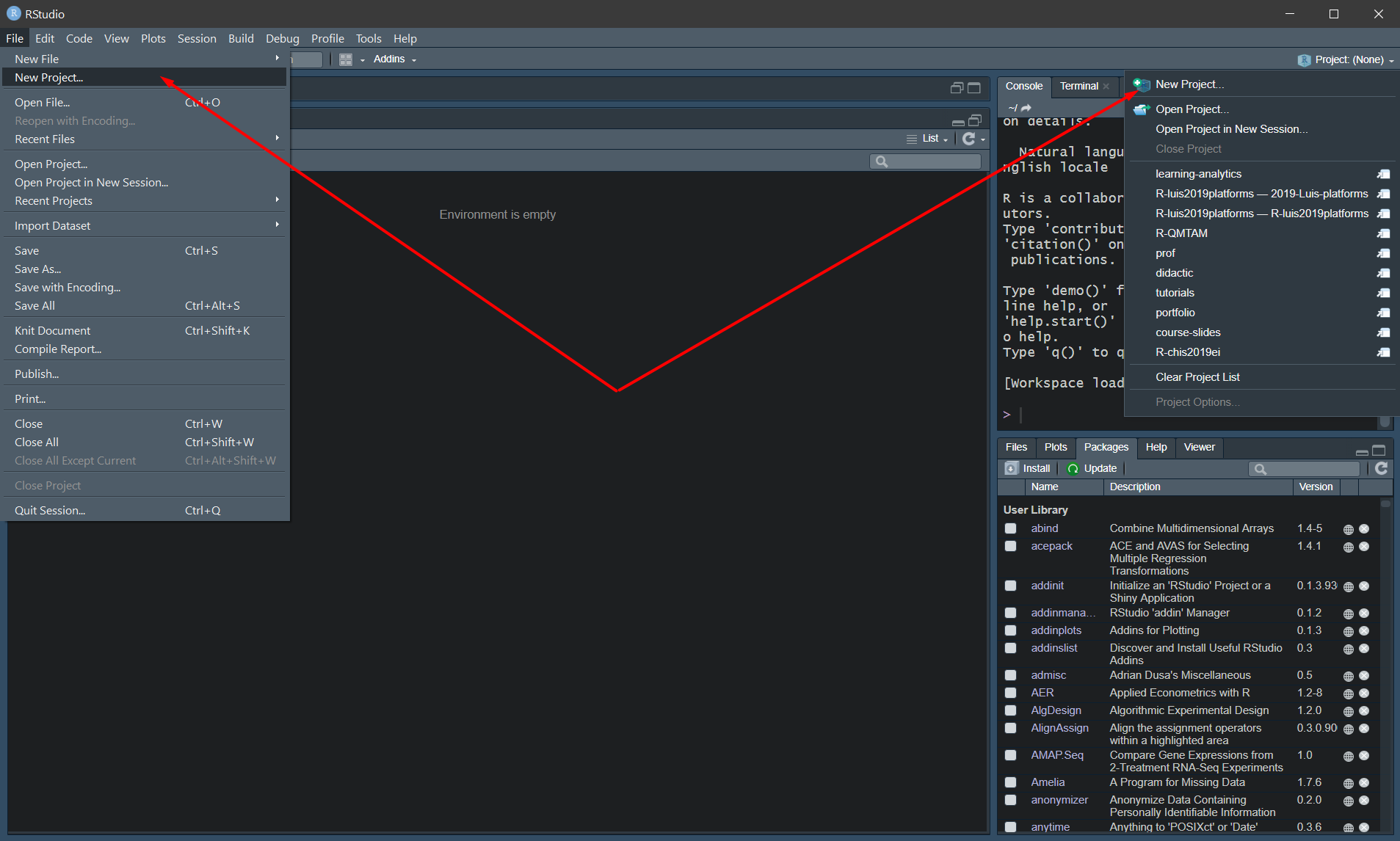
 In RStudio click File, New File, R Markdown. Now that you have a local copy of the repository, let’s add an R Markdown document to your project. Paste the repository URL and enter TAB to move to the Project directory name field. Click File, New Project, Version Control, Git. Open RStudio on your local environment. Click the Copy to clipboard icon to the right of the repository URL. On the right side of the screen, click Clone or download. On GitHub, navigate to the Code tab of the repository. Select Initialize this repository with a README.Īfter you’ve created a repository on GitHub (the remote repository), the next step is to clone it to your local environment. Enter a description for your repository. Note: if your organization uses GitHub Enterprise you can also create the repository there. Now that you have what you need installed locally, let’s create the repository that will hold your new website. Some programming knowledge with R will be helpful but is not required.įor this tutorial you will use Git and RStudio to work with your GitHub repository. If you are new to Git, GitHub and GitHub Pages it is recommended to complete the GitHub Pages from the command-line course first. For this tutorial you will need an account on or GitHub Enterprise. Publish and share your R Markdown documents using GitHub Pages. Use the website or GitHub Enterprise to complete the GitHub workflow. Work with your repository on your local machine using Git and RStudio. GitHub Pages allows you to host websites directly from your GitHub repository. It integrates the tools you use with R into a single environment. RStudio is a popular integrated development environment for R.
In RStudio click File, New File, R Markdown. Now that you have a local copy of the repository, let’s add an R Markdown document to your project. Paste the repository URL and enter TAB to move to the Project directory name field. Click File, New Project, Version Control, Git. Open RStudio on your local environment. Click the Copy to clipboard icon to the right of the repository URL. On the right side of the screen, click Clone or download. On GitHub, navigate to the Code tab of the repository. Select Initialize this repository with a README.Īfter you’ve created a repository on GitHub (the remote repository), the next step is to clone it to your local environment. Enter a description for your repository. Note: if your organization uses GitHub Enterprise you can also create the repository there. Now that you have what you need installed locally, let’s create the repository that will hold your new website. Some programming knowledge with R will be helpful but is not required.įor this tutorial you will use Git and RStudio to work with your GitHub repository. If you are new to Git, GitHub and GitHub Pages it is recommended to complete the GitHub Pages from the command-line course first. For this tutorial you will need an account on or GitHub Enterprise. Publish and share your R Markdown documents using GitHub Pages. Use the website or GitHub Enterprise to complete the GitHub workflow. Work with your repository on your local machine using Git and RStudio. GitHub Pages allows you to host websites directly from your GitHub repository. It integrates the tools you use with R into a single environment. RStudio is a popular integrated development environment for R.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
